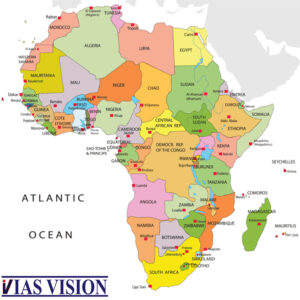
AFRICA PHYSICAL POLITICAL UPSC
Africa Physical upsc geography, CONFLICTS & CIVIL WARS
AFRICA PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY LOCATION AREA
AFRICA PHYSICAL POLITICAL UPSC:
Africa is the second largest among continents in total land area.
Africa has unique geography whereby the equator, the Tropic of Capricorn and the Tropic of Cancer all three imaginary lines pass through it.
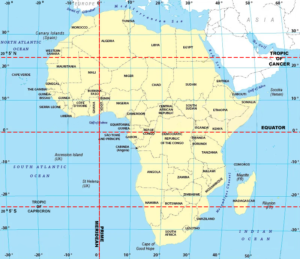

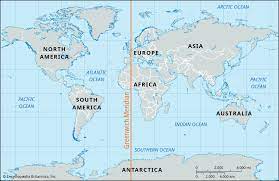
Greenwich Meridian passes through the western part of Africa.
Greenwich meridian passes through England, France and Spain in Europe; Algeria, Mali, Burkina Faso, Togo, and Ghana in Africa; and Antarctica at the South Pole. It intersects the Equator (0° latitude) in the Atlantic Ocean.
Algeria in north is Africa’s largest country by area, and Nigeria also in north is largest country by population & GDP. Seychelles IN INDIAN OCEAN is the smallest country in Africa.
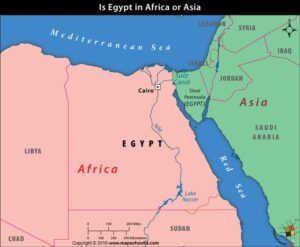
Egypt geographically lies in both Asia & Africa.
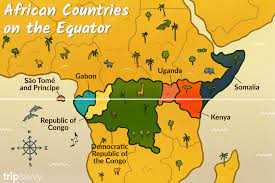
Equator divides Africa virtually into half.
Africa's 3 most recently independent countries,
- Namibia - March 21, 1990, from South Africa
- Eritrea - May 24, 1993, from Ethiopia
- South Sudan -Independence Day: July 9, 2011, from Sudan
African countries old names vs new names;
Historical Country Names:
Historical Country Names
| Former Name | Current Name |
| Abyssinia | Ethiopia |
| Afars and Issas Territory | Djibouti |
| Bechuanaland | Republic of Botswana |
| Belgian Congo | Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| Benadir | Somalia |
| Biafra, Republic of | Nigeria |
| British East Africa | Kenya, Tanzania, Uganda |
| Cape Colony | South Africa |
| Central African Empire | Central African Republic |
| Ciskei (Republic of Ciskei) | South Africa |
| Dahomey | Benin |
| French Somaliland | Djibouti |
| French Sudan | Mali |
| German Southwest Africa | Namibia |
| Gold Coast | Ghana |
| Italian East Africa | Eritrea, Ethiopia, Somalia |
| Katanga | Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| Malagasy Republic | Madagascar |
| Nyasaland | Malawi |
| Portuguese East Africa | Mozambique |
| Rhodesia, Northern | Zambia |
| Rhodesia, Southern | Zimbabwe |
| South-West Africa (SWA) | Namibia |
| Spanish Guinea | Equatorial Guinea |
| Spanish West Africa | Morocco, Western Sahara |
| Tanganyika Territory | Tanzania |
| Togoland (British Togoland) | Ghana |
| United Arab Republic (UAR) | Egypt, Syria |
| Zaire | Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| Zanzibar | Tanzania |
AFRICA TRIBES
AFRICA PHYSICAL POLITICAL UPSC:
TRIBES
North Africa:
- Tuareg - nomadic pastoralists, of Mediterranean countries such as Libya and Algeria as well as countries in the region known as the Sahel, on the Sahara’s southern boundary, such as Niger.
- Bedouin – nomads & desert dwellers of Arabic origin who live in the North East of Africa.
- Dogon - are a branch of the Niger-Congo language group, found in Mali and Burkina Faso.
West Africa:
- Yoruba - Yoruba living almost exclusively in Nigeria’s South West number over 40 million so are comfortably the largest tribe in the whole of West Africa.
- Ashanti - of Ghana are urbanized to a large extent.
- Mbenga - Pygmy Ethnic Group, found in the West Congo Basin.
East Africa:
- Hamer - is a tribe living in Omo Valley of Ethiopia.
- Maasai - of East Africa, particularly Kenya.
- Hadzabe- of Tanzania are the last true nomads, hunter-gatherers of East Africa.
South Africa:
- Zulus - heir language is one of South Africa’s official languages and their home is KwaZulu-Natal on South Africa’s Indian Ocean Coast.
- Himba - small tribe living in Northern Namibia and up into Angola numbers around 50,000.
AFRICA NATIONAL PARKS
AFRICA PHYSICAL POLITICAL UPSC:
National parks in Africa:
- Kruger National Park - one of the largest wildlife reserves in Africa and is located in the northeastern parts of South Africa in the province of Limpopo and Mpumalanga. The park occupies a 19,485 km square and is regarded as a world heritage site by UNESCO.
- Serengeti National Park - is located in Tanzania, stretching all the way to the East Masai Mara regions in Kenya. It is a world famous safari park spanning over the 30,000km square with an unparalleled panorama of vast rolling plains.
- Hwange National Park - is the largest wildlife reserve in Zimbabwe today.
- Masaimara national reserve - is located in the southwest of Kenya, running along the Tanzanian border and occupying a 1,510 km square area. The park is named in honor of the famous Masai tribe.
- Chobe National Park - northern parts of Botswana.
- Kibale forest national park - is located in western Uganda and spans across 776 km square. It is regarded as having the highest concentration of primates in all of Africa because of its impressive array of chimpanzees, red colobus monkeys, and L’Hoest’s monkeys, as well as other endangered species.
- Etosha National Park - Located in the northwest region of Namibia.
- Luangwa National Park - as one of the greatest wildlife sanctuaries in the world. This is because the concentration of animals around the Luangwa River and oxbow lagoons is among the most intense in Africa.
AFRICA PHYSICAL UPSC - WATERBODIES NATURAL & MANMADE
AFRICA PHYSICAL POLITICAL UPSC GEOGRAPHY:
Most of AFRICA is surrounded by water bodies, It is Separated from Europe by Mediterranean Sea, it was connected to Asia in northeast but creation of Suez canal has created the permanent boundary. It is bordered by Indian Ocean to the southeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
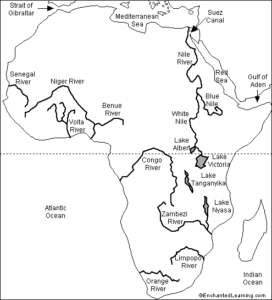
The Nile is a major north-flowing river that flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It travels through eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Sudan, and Egypt.
The Zambezi is the fourth-longest in Africa & longest east-flowing river in Africa and the largest flowing into the Indian Ocean from Africa. The river rises in Zambia and flows through eastern Angola, along the north-eastern border of Namibia and the northern border of Botswana, then along the border between Zambia and Zimbabwe to Mozambique, where it crosses the country to empty into the Indian Ocean. The Zambezi's most noted feature is Victoria Falls.
African Great Lakes are a series of lakes in and around the East African Rift. The series includes,
- Lake Victoria, the third-largest freshwater lake in the world by area;
- Lake Tanganyika, the world's second-largest freshwater lake by volume and depth;
- Lake Malawi, the world's eighth-largest freshwater lake by area; and
- Lake Turkana, the world's largest permanent desert lake and the world's largest alkaline lake.
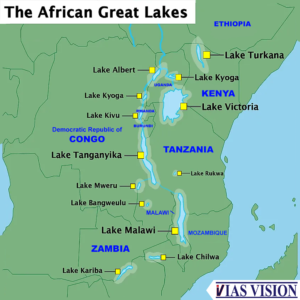
Great Rift Valley lakes
AFRICA PHYSICAL UPSC - Vegetation
AFRICA PHYSICAL POLITICAL UPSC GEOGRAPHY:
Physical regions
- The Sahara Desert - The Sahara is the largest hot desert in the world and the third-largest desert overall, smaller only than the deserts of Antarctica and the northern Arctic. The desert covers much of North Africa, excluding the fertile region on the Mediterranean Sea coast, the Atlas Mountains of the Maghreb, and the Nile Valley in Egypt and the Sudan.
- The Maghreb - The Maghreb is the western part of the Arab world. The region comprises western and central North Africa, including Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. The Maghreb is usually defined as encompassing much of the northern part of Africa, including a large portion of the Sahara Desert, but excluding Egypt and Sudan, Before the establishment of modern nation states in the region during the 20th century, the Maghreb most commonly referred to a smaller area, between the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlas Mountains in the south. Centuries of Arab migration to the Maghreb since the 7th century shifted the demographic scope of the Maghreb in favor of the Arabs.
- The Sahel region - The Sahel region is the transition zone between the more humid Sudanian savannas to its south and the drier Sahara to the north. The Sahel has a hot steppe climate and stretches across the southernmost latitudes of North Africa between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea. Although geographically located in the tropics, the Sahel does not have a tropical climate. Great Green Wall of the Sahara and the Sahel is a project of African union to control expansion of Sahara desert into Sahel, from eastern coast of Djibouti to Senegalese capital Dakar, a distance of 8000 Km, & 15 Km Wide.
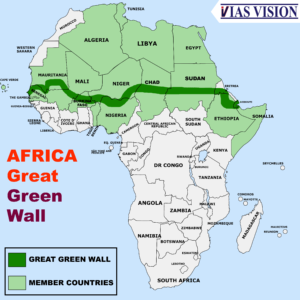
GREAT GREEN WALL AFRICA - The Sudan region - Sudan is the geographical region to the south of the Sahara, stretching from Western Africa to Central and Eastern Africa.
- The Guinea region - Guinea is a traditional name for the region of the African coast of West Africa which lies along the Gulf of Guinea. It is a naturally moist tropical forest or savanna that stretches along the coast and borders the Sahel belt in the north.
- The Congo - The Congo Basin is the sedimentary basin of the Congo River. The Congo Basin is located in Central Africa, in a region known as west equatorial Africa. The Congo Basin region is sometimes known simply as the Congo. It contains some of the largest tropical rainforests in the world and is an important source of water used in agriculture and energy generation.
- The Great Lakes region - African Great Lakes are a series of lakes in and around the East African Rift. The series includes
-
- Lake Victoria, the third-largest freshwater lake in the world by area;
- Lake Tanganyika, the world's second-largest freshwater lake by volume and depth;
- Lake Malawi, the world's eighth-largest freshwater lake by area; and
- Lake Turkana, the world's largest permanent desert lake and the world's largest alkaline lake.
AFRICA PHYSICAL UPSC - LOCAL WINDS
AFRICA LOCAL WINDS UPSC GEOGRAPHY:
Cape Doctor, is dry south-easterly wind that blows on the South African coast from spring to late summer (September to March in the southern hemisphere).
Harmattan, a dry wind that blows from the northeast, bringing dust from the Sahara south toward the Gulf of Guinea.
Khamsin (khamaseen in Egypt) and Haboob in the Sudan, Aajej in southern Morocco, Ghibli in Libya and Tunisia, Harmattan in the western Maghreb, Sirocco, are south winds that blow into Mediterranean sea.
AFRICA PHYSICAL POLITICAL UPSC GEOGRAPHY:
AFRICA DESERTS
List of deserts by region area & country
- Some of Africa’s biggest deserts
| Rank | Name | Type | Location | Nation(s) |
| 1 | Sahara Desert | Subtropical | Eastern Africa Middle Africa Northern Africa Western Africa |
Algeria, Chad, Egypt, Eritrea, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, the Sudan, Tunisia, and Western Sahara |
| 2 | Kalahari Desert | Subtropical | Southern Africa | Botswana, Namibia, and South Africa |
| 3 | Guban Desert | Subtropical | Eastern Africa | Somalia/Somaliland |
| 4 | Namib Desert | Cool coastal | Middle Africa Southern Africa |
Angola, Namibia, and South Africa |
| 5 | Danakil Desert | Subtropical | Eastern Africa | Djibouti, Eritrea, and Ethiopia |
Kalahari Desert - Okavango Delta formed by Okavango (Kavango) River in the Desert is home to some of the world’s most endangered species of large mammal, such as the cheetah, white rhinoceros, black rhinoceros, African wild dog and lion.
AFRICA POLITICAL UPSC - ADMINISTRATION & INSTITUTIONS
AFRICA PHYSICAL POLITICAL UPSC GEOGRAPHY:
Five countries currently under military rule:
- Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso’s military seized power on January 24, 2022, citing neglect of security by former President Roch Marc Christian Kaboré, who was removed from office. The military junta accused Kaboré of corruption and mismanagement. Another coup occurred on September 30, led by Captain Ibrahim Traoré, who is 35 years old. He declared himself president due to the country’s deteriorating security situation.
- Mali
In recent years, Mali has faced several military invasions that have led to instability and insecurity. In May 2021, the military detained President Bah N’Daw and Prime Minister Moctar Ouane, both of whom were appointed after a previous coup in 2020. The country’s security situation has been further aggravated by the rise of terrorist groups, taking advantage of the already fragile state of security in Mali. The interim president of Mali since May 2021 is 42-year-old Colonel Assimi Goita.
- Sudan
Sudan has a long history of political instability, and in October 2022, the country was once again placed under military rule after General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan led a coup. The transitional government was established after the previous President Omar al-Bashir was ousted in 2019 and was disbanded by the military. This has resulted in widespread protests across Sudan and condemnation from around the world. The people of Sudan are demanding the reinstatement of civilian authority and a return to democratic governance. General Abdel Fattah al-Burhan is 62.
- Niger
In August 2023, rebellious soldiers in Niger overthrew the democratically elected administration of President Mohamed Bazoum, further contributing to the growing number of military governments in the Sahel region of West Africa and raising concerns about instability in the area. The region is witnessing an increase in violence from Islamic extremists, leading to a loss of faith in democratic governments. Military coups have followed a similar pattern, in which coup leaders accuse the government of failing to deliver on democratic promises. They pledge to establish a new democratic administration to address these shortcomings, but the process is often delayed. The coup leader is the 62-year-old General Tchiani.
- Gabon
On August 30, 2023, a group of military soldiers in Gabon carried out a coup against the government, taking President Ali Bongo Ondimba into custody and placing him under house arrest. The coup was staged after President Ondimba was declared the winner of an election that would have extended his family’s 55-year rule. The coup leaders claimed that they acted in response to Gabon’s “serious economic and social crisis” and to oppose Bongo’s “authoritarian rule.” The news of the coup attempt caused crowds to gather in the streets of the capital to celebrate. However, the coup has been strongly criticized by the United Nations, the African Union, and other countries such as France, Nigeria, China, and the United States. The alleged coup leader, Brice Nguema is 49 years old.
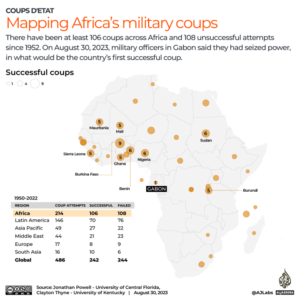
How many coups have there been in Africa?
Out of the 486 attempted or successful military coups carried globally since 1950, Africa accounts for the largest number with 214, of which at least 106 have been successful.
Based on data compiled by American researchers Jonathan M Powell and Clayton L Thyne, at least 45 of the 54 nations across the African continent have experienced at least a single coup attempt since 1950.
African institutions:
ECOWAS - Headquarters - Abuja, Nigeria
-The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS; also known as CEDEAO in French and Portuguese) is a regional political and economic union of fifteen countries located in West Africa.
The union was established on 28 May 1975, with the signing of the Treaty of Lagos, with its stated mission to promote economic integration across the region. A revised version of the treaty was agreed and signed on 24 July 1993 in Cotonou.
The ECOWAS also serves as a peacekeeping force in the region, with member states occasionally sending joint military forces to intervene in the bloc's member countries at times of political instability and unrest.
ECOWAS Member States:
- BENIN
- BURKINA FASO
- CABO VERDE
- CÔTE D’IVOIRE
- THE GAMBIA
- GHANA
- GUINEA
- GUINEA BISSAU
- LIBERIA
- MALI
- NIGER
- NIGERIA
- SENEGAL
- SIERRA LEONE
- TOGO
Chad is currently one of the leading partners in a West African coalition in the fight against Boko Haram and other Islamist militants.Chad's army announced the death of Déby on 20 April 2021, following an incursion in the northern region by the FACT group, during which the president was killed amid fighting on the front lines. Déby's son, General Mahamat Idriss Déby, has been named interim president by a Transitional Council of military officers. That transitional council has replaced the Constitution with a new charter, granting Mahamat Déby the powers of the presidency and naming him head of the armed forces.
FACT - The Front for Change and Concord in Chad ( FACT), is a political and military organisation created by SG Mahamat Mahdi Ali in March 2016 in Tanua, in the north of Chad, with the goal of overthrowing the government of Chad.
The East African Community (EAC)
- an intergovernmental organisation composed of seven countries in the Great Lakesregion of East Africa: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the United Republic of Tanzania, the Republics of Kenya, Burundi, Rwanda, South Sudan, and Uganda. Évariste Ndayishimiye, the president of Burundi, is the current EAC chairman. The organisation was founded in 1967, collapsed in 1977, and was revived on 7 July 2000.
- In 2008, after negotiations with the Southern African Development Community(SADC) and the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA), the EAC agreed to an expanded free trade area including the member states of all three organizations. The EAC is an integral part of the African Economic Community.
- The capital of the EAC is Arusha, Tanzania.
African Union (AU) - )
- is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa.
- AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union.
- The bloc was founded on 26 May 2001 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, and launched on 9 July 2002 in Durban, South Africa.
- The intention of the AU was to replace the Organisation of African Unity (OAU), established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa by 32 signatory governments; the OAU was disbanded on 9 July 2002.
Recent epidemic outbreaks in africa
AFRICA PHYSICAL POLITICAL UPSC GEOGRAPHY:
Epidemic outbreaks in Africa –
The Marburg virus disease (MVD)
ORIGIN – Marburg Frankfurt in Germany
CAUSATIVE AGENT – The Egyptian fruit bat is considered a reservoir for the virus, which can be transmitted through direct contact with infected bat or monkey tissue, bodily fluids, or contaminated objects
AREA OF OUTBREAK – sub-Saharan Africa(Equatorial Guinea and Tanzania)
WHETHER VACCINE AVAILABLE - NO
Ebola virus –
ORIGIN – Ebola River in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo .
CAUSATIVE AGENT – infected animal (bat or nonhuman primate) or a sick or dead person infected with an ebolavirus.
AREA OF OUTBREAK – sub-Saharan AfricaLiberia and Sierra Leone, which border Guinea.
WHETHER VACCINE AVAILABLE – Yes(Ebola vaccine, ERVEBO®, for the prevention of Ebola disease)
